
In North America, Western diets are primarily high in fat, sugar and salt intake; in many cases, these factors can lead to obesity, cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Importantly, mitochondria play a key role in physiology by regulating various glycolysis compounds, including fatty acids and pyruvate, for subsequent ATP production; it must be noted that these fundamental metabolic processes can lead to dysregulation The above diseases. Reconstruction of the mitochondria-associated phosphatidyl chain, the remodeling of the cardiolipin (CL) acyl chain, leads to functional degradation of the basic cardiac metabolic process, but the precise molecular mechanism of this process remains elusive. In this newly published article, Dr. Tonya N. Zeczycki of the University of East Carolina and others used OpenSPR local surface plasmon resonance technology to provide them with the key binding data they found. The data was published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry under the title "Docosahexaenoic acid lowers cardiac mitochondrial enzyme activity by replacing linoleic acid in the phospholipidome". The number of bindings obtained by OpenSPR demonstrates that elevated levels of DHA may be achieved by reducing cardiac mitochondrial enzymes. The activity leads to various metabolic diseases.

ã€Summary】
Phosphatidylinyl chains are involved in the regulation of a series of transmembrane enzymes and membrane-associated enzymes by direct binding. At the time of binding, linoleic acid (LA) and cardiolipin (CL) play a role in this regulatory activity with certain enzyme components of the electron transport chain (ETC); the main interacting protein is protein complex I, III -V and active cytochrome c. Fortunately, these protein-lipid interactions of ETC give absolutely important metabolic stability. However, in the phospholipid structure of mitochondria, acyl chain remodeling may lead to unfortunate dysfunction and may lead to various metabolic diseases. CL accounts for about 15-20% of mitochondrial mass and is considered to be a major player in the phenomenon of abnormal acyl chain remodeling.
In addition, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), an omega-3 fatty acid, has been extensively studied and promoted as a cause of improvement in risk factors for macular degeneration, neuroinflammation, neurodegenerative and cardiovascular diseases; Below, the researchers here believe that at high levels, DHA may help reduce cardiac mitochondrial activity, leading to metabolic dysfunction.
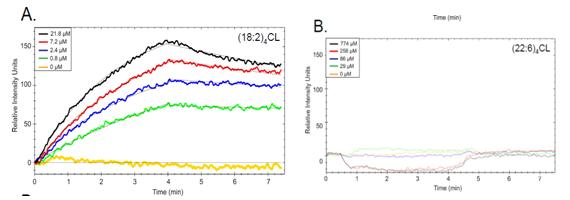
In this article, the researchers constructed a bionic mitochondrial large unilamellar vesicle (LUV) similar to the mitochondrial inner membrane composition. According to the characteristics, the interaction of LUVs containing (18:2)4CL and (22:6)4CL structures with complex IV of ETC transmembrane proteins was detected, and the (22:6)4CL levels of rodents exposed to dietary DHA were selected. Raise. It should also be noted that prior to conducting biophysical studies, the researchers observed that complex IV activity after exposure to DHA became low. The results of the study indicate that the binding of LUV constructed from reconstituted (22:6) 4CL to complex IV is significantly different from that of unreconstructed (18:2) 4CL constructed LUV.
The OpenSPR kinetic assay structure indicated that the CL-specific binding site of complex IV could not bind to the reshaped (22:6)4 CL; it should be noted that these binding sites were considered to be high affinity sites.
The key role of OpenSPR in this research
The interaction of LUVs with different components of CL and complex IV was measured by surface plasmon resonance (SPR), complex IV in solution was immobilized on a carboxyl sensor, and protein-lipid experiments were performed on an OpenSPR instrument. Using OpenSPR, the researchers were able to determine the kinetic data (binding and dissociation rate constants, equilibrium constants and affinities) of the interaction between (18:2) 4CL and (22:6)4CL LUVs and immobilized complex IV. The SPR binding curve shows that (18:2) 4 CL-type LUVs have an effective interaction with complex IV and an equilibrium dissociation constant (KD) of 1.8 μM. Significantly, no binding was detected between (22:6)4 CL-type LUVs and complexIV, and the results indicated that the complex IV binding site could not bind to the reconstituted CL. It should also be noted that the complex enzyme function of complex IV is restored after the introduction of linoleic acid. Accordingly, the results of this study suggest that elevated levels of DHA in cardiac tissue may result in loss of ETC enzyme function, leading to the development of many metabolic diseases. By using OpenSPR, researchers can obtain SPR data from their own lab platforms, speeding up their research and publishing their findings faster.
Why is SPR important for publishing articles? How can OpenSPR help?
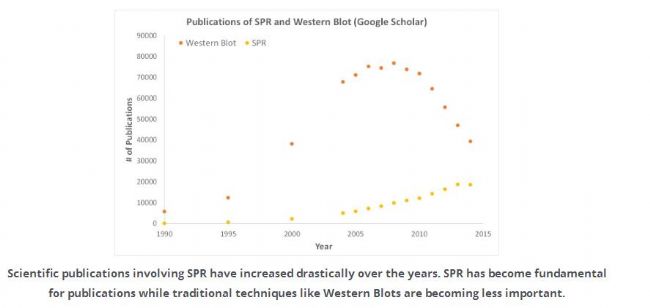
SPR is an unlabeled detection technology that allows researchers to quantify the binding between two biomolecules. The SPR technique allows us to determine the interactions of kon, koff and KD, and provides a deeper understanding of the interactions between molecules compared to other techniques that provide only endpoint measurements (such as pull measurements). SPR is not only necessary for publishing articles, but also necessary for the development of many medical and medical research fields. As shown in the following figure, the number of articles published by SPR data has increased significantly in recent years.
OpenSPR is a user-friendly and low-maintenance, low-tech threshold for next-generation SPR solutions that are currently used by hundreds of researchers. With LSPR technology at your fingertips, you can get the quality data you need while speeding up your research and publishing!
Advantages of Nicoya OpenSPR Molecular Interaction in Cardiovascular Disease Research:
• Easy to operate - 1 hour to control;
• Complete kinetic parameter detection --- Ka, Kd, ​​KD;
• High efficiency --- loading, results, one-click analysis, 10min results, 1-2h complete kinetic test results;
• High precision--- detection is not affected by temperature and buffer refractive index;
• No special correction channel required - negligible bulk effect;
Consistent and accurate readings during blood pressure monitoring
Ibp Transducer,Ibp Interface Cable,Double Line Ibp Transducer,Invasive Blood Pressure Transducer
Zhejiang Haisheng Medical Device Co., Ltd , https://www.hisernmedical.com