The latest results! Gradually inhibit BACE1 enzyme activity, can reverse dementia
February 23, 2018 Source: Biological Exploration
Window._bd_share_config={ "common":{ "bdSnsKey":{ },"bdText":"","bdMini":"2","bdMiniList":false,"bdPic":"","bdStyle":" 0","bdSize":"16"},"share":{ }};with(document)0[(getElementsByTagName('head')[0]||body).appendChild(createElement('script')) .src='http://bdimg.share.baidu.com/static/api/js/share.js?v=89860593.js?cdnversion='+~(-new Date()/36e5)];To treat Alzheimer's disease, scientists have found many goals. Among them, β-amyloid lyase (BACE) is one of the hot targets. Recently, an article in the Journal of Experimental Medicine revealed that the gradual inhibition of BACE1 enzyme can completely eliminate the formation of amyloid plaques in the brain of mice and improve their cognitive and memory abilities.

Image source: Network
The study, completed by scientists at the Lerner Institute at the Cleveland Clinic, provides support for the development of anti-dementia drugs that target BACE1.

DOI: 10.1084/jem.20171831
1 , β- amyloid lyase
Excessive accumulation of β-amyloid in the brain is a typical pathological feature of Alzheimer's disease, and the BACE1 enzyme is a key enzyme (the amyloid precursor protein APP) that produces this protein. Therefore, BACE1 enzyme is considered to be a hot target for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
However, given that BACE1 is involved in the molecular reaction processes of multiple proteins (in addition to APP), scientists are concerned that such drugs can cause serious side effects. Earlier, Merck's Verubecestat was the first BACE1 inhibitor to enter clinical stage III, but did not receive positive clinical results in the treatment of mild to moderate dementia.
In addition to treatment, BACE1 is also considered to be an important marker for predicting and diagnosing the occurrence and development of Alzheimer's disease and is currently under investigation.
2 , the latest research
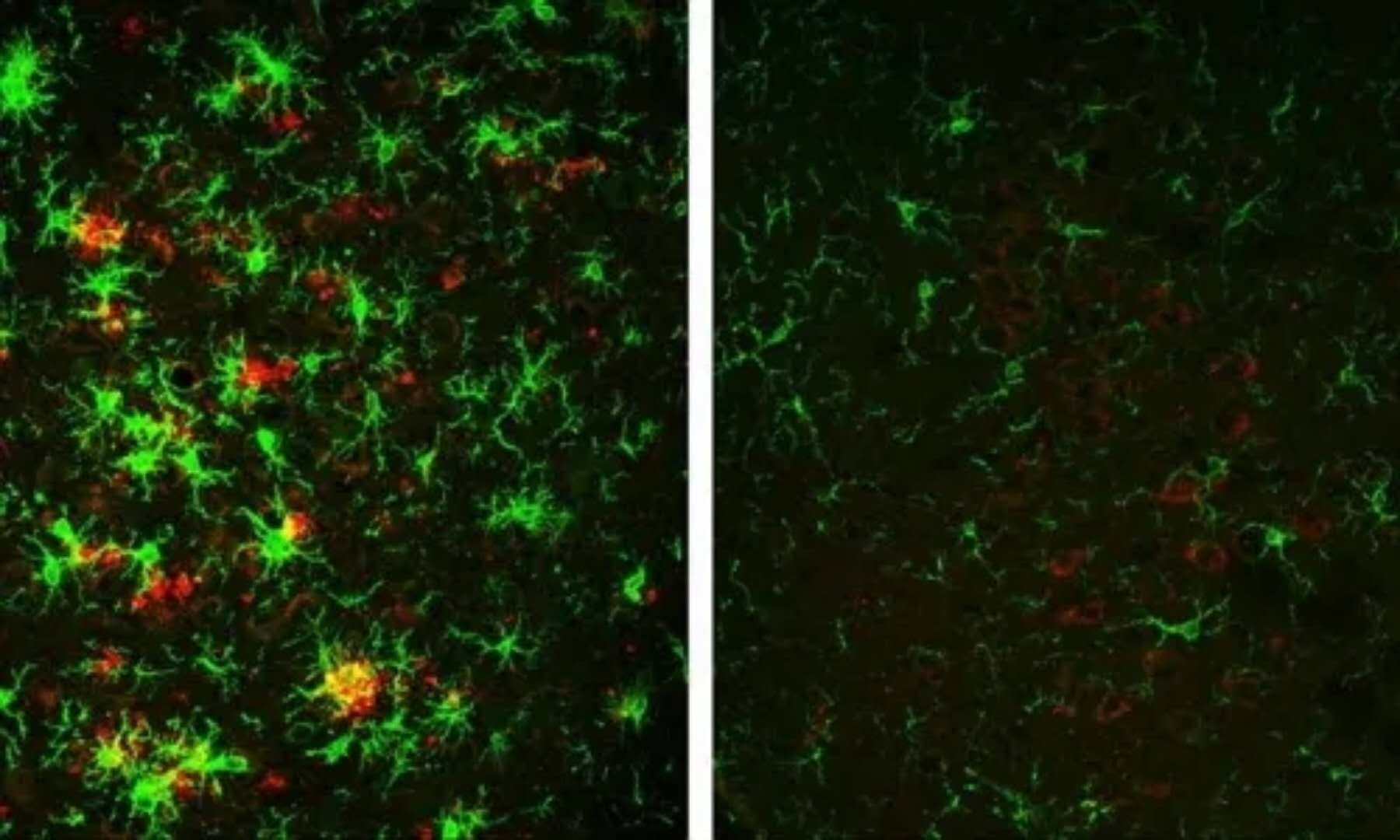
The brain of a 10-month-old mouse with Alzheimer's disease (left) is full of amyloid plaques (red) surrounded by activated microglial cells (green).
But these hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease are reversed in animals that have gradually lost the BACE1 enzyme (right). Credit: Hu et al., 2018
The author of the article, Riqiang Yan, led the team to find that complete inhibition of BACE1 triggers severe neurodevelopmental defects in mice. However, with the aging of mice, the BACE1 enzyme activity is gradually inhibited, which is beneficial to the health of mice.
When 75-day-old adult mice begin to develop symptoms of Alzheimer's disease (amyloid plaques are detected in the brain), their offspring will also develop the same condition at this age, even if their BACE1 enzyme activity is lower than normal. 50%. However, it is worth noting that as the mice continue to age and BACE1 activity continues to decrease, the protein lesions in the brain begin to disappear until no lesions are present (10 months old).
Inhibition of BACE1 enzyme activity can reduce β-amyloid levels and reverse other conditions of dementia, such as activation of microglia, abnormal neurodegeneration. Moreover, silencing of the BACE1 enzyme can improve the learning and memory ability of dementia mice.
"Our data suggest that adult mice gradually reverse the deposition of pathogenic proteins after gradually inhibiting BACE1 activity. This means that BACE1 inhibitors have the potential to treat Alzheimer's disease without serious side effects." Riqiang Yan emphasized.
References: 1) Researchers successfully reverse Alzheimer's disease in mouse model
Personal Care,Hair Conditioner,Body Wash Shower Gel,Moisturizing Shower Gel
Wuxi Keni Daily Cosmetics Co.,Ltd , https://www.kenidailycosmetics.com