 Principles of Photosynthetic Effective Optical Radiation Testing--PAR, PPF, PPFD
Principles of Photosynthetic Effective Optical Radiation Testing--PAR, PPF, PPFD
 Sunlight is essential for plants because plants need to rely on sunlight for photosynthesis. We all know that sunlight is a source of continuous spectrum, and photosynthesis of plants is mainly carried out in the visible spectrum. With the advancement of technology, people gradually produce corresponding standard light sources based on the continuous spectral characteristics of natural light. According to the growth characteristics of plants, people gradually produce plant light sources that can replace natural light to promote photosynthesis of plants. However, the position lights produced are not necessarily consistent with natural light. How to evaluate the characteristics of plant light sources, lumens, lux These parameters of the candlelight have become an outdated indicator for determining the requirements of light for plants. Recently, people began to measure the photosynthesis light illumination application by PAR, PPF and PPFD methods. According to the various illuminometers I have used, the condensed luminosity meter GL
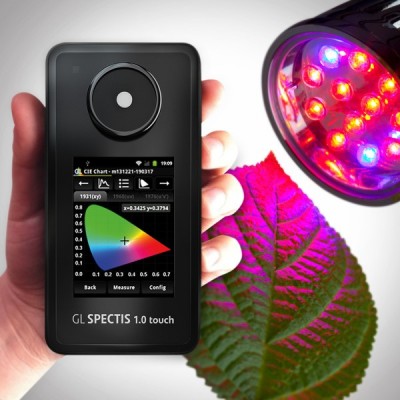
Sunlight is essential for plants because plants need to rely on sunlight for photosynthesis. We all know that sunlight is a source of continuous spectrum, and photosynthesis of plants is mainly carried out in the visible spectrum. With the advancement of technology, people gradually produce corresponding standard light sources based on the continuous spectral characteristics of natural light. According to the growth characteristics of plants, people gradually produce plant light sources that can replace natural light to promote photosynthesis of plants. However, the position lights produced are not necessarily consistent with natural light. How to evaluate the characteristics of plant light sources, lumens, lux These parameters of the candlelight have become an outdated indicator for determining the requirements of light for plants. Recently, people began to measure the photosynthesis light illumination application by PAR, PPF and PPFD methods. According to the various illuminometers I have used, the condensed luminosity meter GL  Spectrolux is more suitable for measuring plant photosynthesis effective radiation parameters and photon flux density, and the condensed spectral illuminometer can be used to evaluate the spectral characteristics of plant light sources. A good-performing plant lamp is a plant that determines the proper light level to promote rapid and prosperous plant growth. How to determine the characteristics of a plant lamp and how to choose a spectrophotometer is a key factor. Let's talk about the spectrophotometer Spectrolux. Discuss the basic principles of plant photosynthesis effective radiation (PAR, PPF, PPFD).
Spectrolux is more suitable for measuring plant photosynthesis effective radiation parameters and photon flux density, and the condensed spectral illuminometer can be used to evaluate the spectral characteristics of plant light sources. A good-performing plant lamp is a plant that determines the proper light level to promote rapid and prosperous plant growth. How to determine the characteristics of a plant lamp and how to choose a spectrophotometer is a key factor. Let's talk about the spectrophotometer Spectrolux. Discuss the basic principles of plant photosynthesis effective radiation (PAR, PPF, PPFD).

The first measurement is photosynthetic photon flux or "PPF", which measures the total amount of light produced per second by a single source. In other words, the PPF tells us what the standard is for a light source to emit per second. Technically, the PPF measures "photons synthesized by the light emitted by the illumination system per second." This measurement is expressed in terms of "micropores per second". However, PPF does not tell us how much of the measured light is on plants or other surfaces.
The second measurement method is PPFD to measure light reaching plants or algae. Photosynthesis photon flux density or "PPFD" is the measure of the amount of light actually reaching plants and algae, or scientists may say: "The number of photosynthesis photons that occur per second on a given surface." PPFD is a Point "measures a specific location on the canopy of your plant, measured in micropores per square meter per second. This measurement method is represented by scientists and optical engineers: mol/m2/s.
The third measurement method is DLI (daylight integration), which measures the total amount of light delivered to the plant per day. Growers can think of DLI as the “dose†of plants every day, although scientists may say that DLI is a cumulative measure of the total number of photons that reach plants and algae during daily light operations. DLI measures the "molar" number of photons per square meter and is expressed as: moles per square meter.
DLI is similar to the total amount of rain during a storm, with the speed of rainfall (this is PPFD). The most important indicator of DLI is to determine the overall growth rate of plants and algae. Once you know the preferred DLI for your plant or algae, you can easily set up an illumination system to provide the amount of light you need.
There are a lot of photons or light particles in visible light - in fact, the quantity is so large that we can't express it with normal numbers, so we used two common measurement methods to measure a large amount. The first number, which is called mole, is equal to one called Avogadro's number, which is 602144150000000000000000! For a number that is easier to control, the micromolar is one in ten thousandth of a mole.
PPF tells us how many photons are emitted by a light source every second. PPFD tells us that this device distributes photons to a one-meter target (ie your plants and algae) in one second. DLI tells us how many photons are transmitted to a one-meter target (ie one day) in a complete photoperiod.
Every aquarium and lighting system is different, and there are many factors that affect the total amount of light in the fixture. Although lumens are easy to measure, they have nothing to do with the amount of light given to plants and algae. PAR, PPF PPFD, DLI are precise and consistent terminology and measurement methods used by scientists, algae researchers, horticulturists and laboratories. PPF tells us how many photons per second are produced by a lighting device, but it does not tell us where these photons land. This is why we need PPF density or PPFD.
Define photosynthesis radiation (PAR), which is not a measure or measure, like feet, inches or kilograms. PAR defines the type of light needed to support photosynthesis in plant life. Photosynthetic photon flux (PPF) measures the total light (photons) emitted by the source per second. PPF tells us what the standard is for a light source. It is measured in microseconds and is expressed as: moles per second. Photosynthetic photon flux density (PPFD), which measures the light (photons) that reach the target every second. PPFD is measured in an area of ​​1 meter per square meter per second and is expressed in moles/m2/s. Daylight Integration (DLI) accumulates the total amount of light (photons) of the measured light (photons) and reaches the target during light operation. DLI is measured in moles per square meter in m/m2/d. Photons are the names of physicists giving light particles. Natural or artificial light can be used to promote photosynthesis of plant life.

The growth rate of the organism is directly affected by light irradiation. The ultraviolet light with a wavelength of 300-400 nm and the near-infrared light of 700-800 nm (far red light) affect the biochemical reaction and appearance of the organism. Especially in the light of 400~700nm, the photosynthesis of plants and algae is closely related. The light of this spectrum is called Photosynthetically Active Radiation (PAR).
The preferred measurement basis for the number of photons in the range of photosynthesis effective light (PAR) is to measure its photosynthetic photon Flux Density (PPFD), which is in the range of 400-700 nm in wavelength per unit time. The number of photons falling on a unit area is commonly used in μmol/(secm2) or μE/(secm2).
The figure below shows the Spectrolux, a solid-state spectrophotometer that measures radiation from the sun and other sources and measures the energy at wavelengths in the range of 340 to 780 nm. The measured value is W/m2. Its Sensor simulates a photosynthetically effective function to exactly match the needs of the application. At present, most foreign products also use this as the product design direction to meet the needs of professional users.
Radiation illuminance measurement range: 0.03 to 600 w/m2 (convertible to μmol / m2 or μE / m2·s or Photon/m2·s)
Illuminance measurement range: 1 lx to 200.000 lx
Why 380~700nm?
The wavelength of natural light is 380~700nm, which is also the most suitable wavelength range for aquatic plants. A light with a wavelength of less than 400 nm called ultraviolet light has a certain influence on the water grass, and it is a negative influence. 7% of the ultraviolet light can be divided into three different wavelengths (both have different effects on aquatic plants): C-grade ultraviolet (200-280) accounts for 3% - harmful to most aquatic plants; B-grade ultraviolet (280-320) ) 9% - harmful to most aquatic plants; A-grade ultraviolet (320-380) accounted for 88% - beneficial to aquatic plants, so that the thickening of the leaves has a bactericidal effect. Recommended instruments: artificial climate chamber, artificial climate incubator. The artificial climate incubator is an instrument that can set the temperature, humidity and illuminance by itself, that is, the parameter that can control the environmental factors of the water grass - the light, which brings great relationship between the study of the relationship between plants and light. Convenience.

The light that has a greater impact on aquatic plants is mainly in three categories. Ultraviolet, visible and infrared. Below we will specifically analyze these three categories of light.
Radiation light in the first band: It is ultraviolet light containing a lot of energy, but some of the ultraviolet rays are absorbed by the ozone layer. Therefore, we are more concerned with the parts that are closely related to the agricultural film: ultraviolet-b (wavelength 280-320nm) and ultraviolet-a (wavelength 320-380nm). These two bands of ultraviolet light have different effects such as: Plant flowers produce a coloring effect.
Radiation light in the second band: visible light (wavelength 400-700 nm), equivalent to blue light, green light, yellow light, and red light, also known as PAR, which is an active area for photosynthesis. It is the most important visible part of the plant used for photosynthesis. Blue light and red light are the most important parts of the PAR spectral band, because riboflavin in plants can effectively absorb this part of the light, while green light is not easily absorbed.
Radiation light in the third band: it is infrared light, and it can be divided into near infrared rays and far infrared rays.
Light in the near infrared (wavelength 780-3,000 nm) is basically useless to plants, it only produces heat.
Far infrared rays (wavelength 3000-50,000nm), this part of the radiation is not directly from the sun. It is a kind of radiation generated by molecules with thermal energy that is easily lost at night.
The sensitivity of aquatic plants to the spectrum is different from that of the human eye. The most sensitive spectrum of the human eye is 555 nm, which is between yellow and green. It is less sensitive to the blue zone and the red zone. Water plants are not the same, most sensitive to red light spectrum, less sensitive to green light, but the difference in sensitivity is not as disparate as the human eye. The most sensitive area of ​​water plants is 400~700nm. This segment spectrum is often referred to as the photosynthetically active energy region. About 45% of the energy of sunlight is in this spectrum. Therefore, if an artificial light source is used to supplement the amount of light, the spectral distribution of the light source should also be close to this range.
The photon energy emitted by the light source varies with wavelength. For example, the energy of a wavelength of 400 nm (blue light) is 1.75 times the energy of 700 nm (red light). But for photosynthesis, the effect of the two wavelengths is the same. The excess energy in the blue spectrum that cannot be used as photosynthesis is converted into heat. In other words, the photosynthesis rate of aquatic plants is determined by the number of photons that can be absorbed by plants in the 400-700 nm range, and is not related to the number of photons sent by each spectrum. But most people's general knowledge believes that light color affects the rate of photosynthesis. Aquatic plants have different sensitivities for all spectra. This reason comes from the special absorption of pigments in the leaves. Among them, chlorophyll is most known. But chlorophyll is not the only pigment that is useful for photosynthesis. Other pigments are also involved in photosynthesis, so photosynthesis efficiency cannot be based solely on the absorption spectrum of chlorophyll.
The differences in photosynthesis paths are also not related to color. Light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll and carotene in the leaves. Energy is converted to glucose and oxygen by fixed moisture and carbon dioxide by two photosynthetic systems. This process takes advantage of the spectrum of all visible light, so the effects of light sources of various colors on photosynthesis are almost the same.
Some researchers believe that there is maximum photosynthesis in the orange-red portion. However, this does not mean that plants should be cultivated in such a monochromatic light source. For plant morphological development and leaf color, plants should receive a variety of balanced light sources.
Blue light sources (400~500nm) are important for plant differentiation and stomata regulation. If the blue light is insufficient, the proportion of far red light is too much, and the stem will grow excessively, which is likely to cause yellowing of the leaves. The ratio of red light spectrum (655~665nm) energy to far red light spectrum (725~735nm) energy is between 1.0 and 1.2, and plant development will be positive. But each plant is also sensitive to these spectral proportions.

Combined with the solid-state spectrophotometer, Spectrolux can measure the effective radiation of photosynthetic photosynthesis and the photon flux density, and provide solutions to meet the needs of industrial applications. The Spectrolux is a solid-state spectrophotometer that produces accurate measurements on LED displays in seconds for quick evaluation. Handheld portable spectrophotometers can be used to evaluate the rapid control of lighting fixtures and LED fixtures, and even support application and sales engineers to quantify modern lighting systems. Spectrophotometers are used in high-end laboratory, R&D and feed quality control to provide lighting professionals with simple and reliable spectroradiometers to provide solutions for industrial applications.
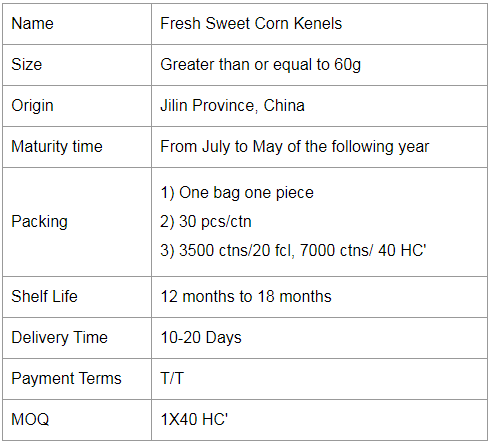
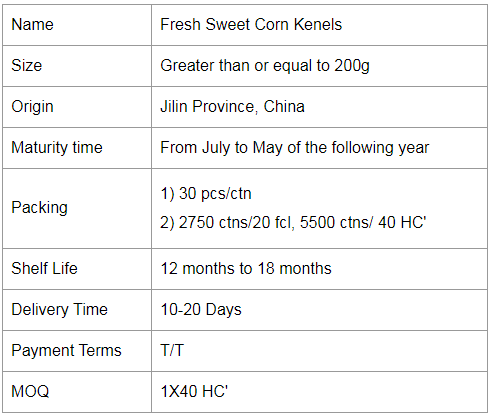
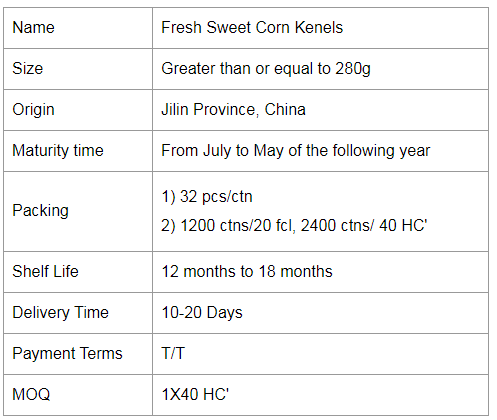
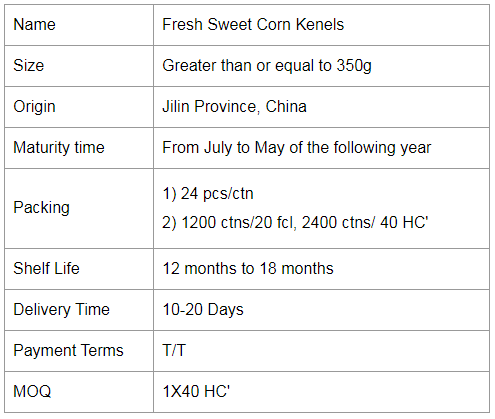
Ready-to-eat Sweet Corn Kernels
In one sunny morning, a sweet corn or glutinous corn is a good choice for breakfast to kick-start the day. Corn has a richer taste than other staple food. Glutinous corn has a sweet and waxy taste. It's also a filling food to fill up for the day, supplement the nutrition that the human body needs.
Fruit corn. The outer leaves are pale green, and the inner grains are white or yellow.The sweetness is higher than sweet corn, but the starch content is low, rich in vitamin E and cellulose, can fight aging and help digestion.Ideal for raw food, mixed with vegetables into salad;It can also be steamed, but don't cook it for too long, about five minutes.


If you would like to work with us, please send us a message on the website or contact us by email.
Fresh Corn Kernels,Corn Whole Kernel,Boiled Corn Kernels,Baby Corn Kernels
Jilin Province Argricultural Sister-in-law Food Co., Ltd. , https://www.nongsaocorn.com