1. Nursery fat
The planting of string beans is mainly live broadcast. With the development of cultivation techniques for string beans in protected areas, methods for transplanting seedlings have gradually become popular. The nutrient soil used for nursery should be the vegetable garden soil that has not been planted with green beans for 2 to 3 years. It is made by mixing 4 parts of vegetable garden soil with 4 parts of rotted horse manure and 2 parts of rotted chicken manure. Then add 2 to 3 kg of superphosphate and 0.5 to 1.0 kg of potassium sulfate. Soil acidity and alkalinity should be neutral or weakly acidic. Soil overacidity will inhibit the activity of rhizobia on acidic soil. Appropriate lime can be used to neutralize acidity. Mix lime with bed soil when applying lime. Do not use too much. Large or uneven mixing can easily cause burning seedlings and ammonia volatilization, causing gas hazard.
2. Base fertilizer
String beans are fat crops in beans. Although they have nodules, the nitrogen fixation is weak. In the seedling stage of rhizobia, use the available nutrients in the base fertilizer to promote plant growth and development, generally use 4000-5000 kg of manure per acre, or 5000 kg of decomposed organic fertilizer, 20-35 kg of superphosphate, grass ash 100 kg.
The basic fertilizer of dwarf string beans can be reduced appropriately. Roots of string beans have higher requirements on soil oxygen. The application of unrotted chicken manure or other organic fertilizers will increase the reducing gas of the soil and reduce the oxygen, causing rotten seeds and premature aging of the root system, which has a great impact on yield. Therefore, applying base fertilizer should pay attention to the selection of fully decomposed organic fertilizer, and it is not suitable to use too much nitrogen fertilizer as seed fertilizer.
3. Topdressing
Green beans 20 to 25 days after planting, when the flower bud differentiation of green beans begins, if there is no sufficient base fertilizer, the green beans show symptoms of lack of fertilizers, and topdressing should be carried out in time, applying 20% ​​to 30% of biogas slurry per mu for about 1500 Kilograms, potassium sulfate can also be added 4 to 5 kilograms per 1000 kilograms of dilute manure. Early application of top dressing has obvious effect on yield increase, but applying too much nitrogen fertilizer at the seedling stage will make green beans long. Therefore, whether top dressing should be based on plant growth.
Green beans require the most fertilizer during the flowering and podding period. The nutrients of the vine varieties during the podding period mainly come from root absorption, and some of them are transported from the stems and leaves, and the flowering and podding periods are longer. The nutrients at the pod stage are transported by stems and leaves higher than those absorbed by the roots. Therefore, vines require a larger amount of fertilizer than dwarf varieties, and the number of fertilizations must increase accordingly. Generally, dwarf green beans are top-dressed 1 to 2 times, and overgrown green beans are applied 2 to 3 times. Each time topdressing urea 7~11 kg, potassium sulfate 10~15 kg, the dosage of the last nitrogen fertilizer is halved, and the dosage of potassium fertilizer can also be halved or not applied.
4. Matters needing attention
The fast-acting nutrients are needed at the seedling stage of string beans, so the basal fertilizer should be rotted organic fertilizer, a small amount of nitrogen fertilizer, and phosphorus and potassium fertilizers. The fertilizer is turned into the soil and then ridged. The amount of base fertilizer for dwarf varieties is about 80% of vine growth. However, it should be noted that adding too much nitrogen fertilizer to the base fertilizer will cause the plant stem and leaf tissues to be young and long. For the cultivation covered with plastic film, the amount of basal fertilizer should be increased appropriately compared with open cultivation because of inconvenient top dressing.
Disclaimer: Some articles of this website are transferred from the Internet. If the legal rights of third parties are involved, please inform this website for processing. phone
A medium-sized cob of corn provides more than 10% of our daily dietary fibre requirements.
There are two types of dietary fibre - soluble and insoluble - and sweet corn contains both.
According to the American Heart Association, dietary fibre as part of an overall healthy diet can help lower blood cholesterol levels and may reduce the risk of heart disease. It is insoluble fibre that binds to cholesterol, preventing it from being absorbed into the bloodstream.
Insoluble fibre is responsible for promoting regularity and helping to prevent constipation by speeding up the passage of food and waste through the intestines and absorbing water to keep stools soft. Insoluble fibre has been shown to reduce the risk of haemorrhoids.
Fibre-containing foods such as sweetcorn also help to provide a sense of satiety and may therefore help to suppress appetite and aid weight management.
Dietary fibre has also been linked to a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes. A diet rich in fibre helps patients manage their disease.
Fibre is fermented by bacteria in the colon. Promising studies are underway to determine the health-promoting effects of fibre fermentation breakdown products, for example, short-chain fatty acids, which may help to maintain a healthy gut.
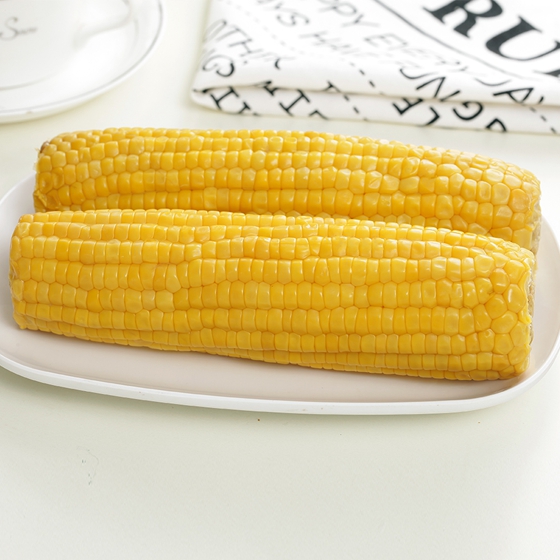

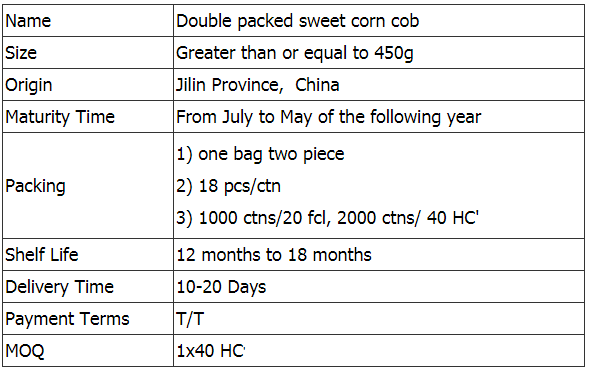
Yellow Sweet Corn,Double Packed Sweet Corn,Double Packed Sweet Corn Cob,Double Packed Yellow Sweet Corn
Jilin Province Argricultural Sister-in-law Food Co., Ltd. , https://www.nongsaocorn.com