Genome Research丨lncRNA plays an important role in spermatogenesis
Non-coding RNA (ncRNA), which has been regarded by many scientists as "junk" information in the evolution of eukaryotic genomes, does not encode proteins, but lacks genetic evidence of biological functions. In recent years, it has been "rehabilitated". The more studies show that ncRNA plays an important role in many life activities such as dose compensation effect, epigenetic regulation, cell cycle regulation and cell differentiation regulation, and has become a hot research topic in genetics.
With the development of high-throughput sequencing technology, more and more lncRNAs have been shown to exhibit highly specific expression in testis and brain tissue, suggesting a functional mechanism of lncRNA during two basic life processes of spermatogenesis and neuromodulation. Representative.
The Tsinghua University High Champion Laboratory officially published an article entitled "Critical roles of long noncoding RNAs in Drosophila spermatogenesis" at Genome Research on September 1, 2016. This article elaborates on the important role of lncRNA in spermatogenesis and provides a large amount of genetic evidence for revealing that "dark matter lncRNA" has important biological functions.
The high-champion research team selected the gene-purified model organism, Drosophila, to identify 128 testicular-specific expressions of lncRNA through the establishment of a high-throughput genetic animal model. Then 105 optimized lncRNA gene knockouts were established using optimized CRISPR technology. By observing and analyzing the spermatogenesis, development and vitality of male Drosophila, it was found that nearly one-third of the lncRNA gene deletion leads to abnormal sperm development or even complete infertility.
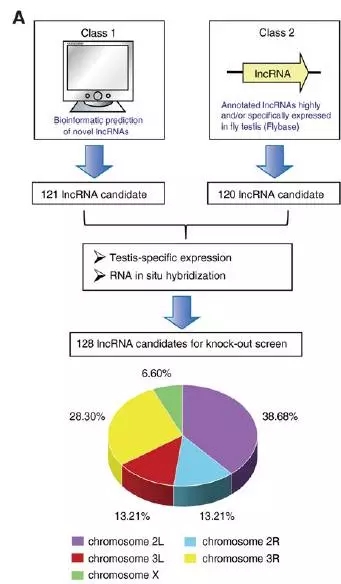
Figure 1. Flowchart of identification and selection of testicular-specific lncRNA in the knockout study. A novel lncRNA combination of bioinformatics and analysis of lncRNA annotated in FlyBase was used to construct a lncRNA starting library. Then, 128 testicular-specific lncRNA candidates were selected for targeted knockout by testicular-specific expression screening and RNA in situ hybridization. These lncRNAs are located on three different chromosomes, including the left and right arms of chromosome 2, the left and right arms of chromosome 3, and chromosome X.
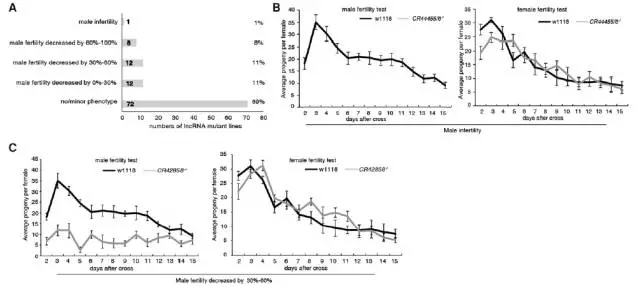
Figure 2. The lncRNA mutant results in a male-specific reproductive defect. (A) Fertility profile of 105 lncRNA mutants. (B) Deletion of lncRNA CR44455 / 6 leads to male sterility, while CR44455 / 6 - / - females are fully fertile. (C) Qualitative fertility determination of male and female mutant flies of CR42858 - / -. The deletion of CR42858 greatly reduced the fertility of males, but females were not affected.
However, it was found by ectopic transgenic methods that the fruit flies knocked out by lncRNAs can completely or partially repair abnormalities, indicating that these lncRNAs mainly function in trans. The high-champion team also analyzed gene expression profiling that most functional lncRNAs regulate global gene expression during spermatogenesis. Evolutionary analysis showed that lncRNAs evolved faster than the coding genes, and lncRNAs with greater functional importance have higher sequence conservation, suggesting that they are under constant evolutionary selection. Different from the switch regulation of protein-coding genes, lncRNA may regulate the global gene expression through fine-tuning, which affects male germ cell differentiation.
The significance of this research in the high-champion group is to make up for the lack of genetic evidence for the large number of functional lncRNAs at the living level of animals, opening the door to life information research transmitted by lncRNA. Next, I will attach a summary of this article for everyone.
Summary:
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), a recently discovered class of cellular RNAs, play important roles in the regulation of many cellular developmental processes. Although lncRNAs have been systematically identified in various systems, most of them have not been functionally characterized in vivo in animal models In this study, we identified 128 testis-specific Drosophila lncRNAs and knocked out 105 of them using an optimized three-component CRISPR/Cas9 system. Among the lncRNA knockouts, 33 (31%) exhibit a partial or complete loss of male fertility, In addition, six knockouts were fully or partially rescued by transgenes in a trans configuration, indicating that those lncRNAs primary work in trans. further, gene expression profiles for five lncRNA mutants revealed that testis-specific lncRNAs Regulate global gene expression, orchestrating late male germ cell differentiation. Compared with coding genes, the testis -specific lncRNAs evolved much faster., lncRNAs of greater functional importance exhibit higher sequence conservation, suggesting that they are under constant evolutionary selection. Collectively, our results reveal critical functions of rapidly evolving testis-specific lncRNAs in late Drosophila spermatogenesis.
High Champion Profile :
Senior Champion, PI, Ph.D., School of Life Sciences, Tsinghua University. In June 2005, he obtained a Ph.D. in biophysics from Zhejiang University. Since 2011, he has been employed as a PI and doctoral tutor by the School of Life at Tsinghua University. At present, through the use of the laboratory's internationally established CRISPR and phiC31 recombinase-binding high-efficiency fly gene targeting system (knock-out and knock-in), the combination of genetic and biochemical methods and techniques, scale To study the biological functions and corresponding molecular mechanisms of chromatin epigenetic related factors (such as non-coding RNA and histone modification) in the reproductive system and early embryonic development. The research results have been published many times in international academic journals such as Nature, Genome Research, PNAS, EMBO J, Genetics, G3: Genes|Genomes|Genetics, Nature Microbiology.
Related meeting recommendations
2017 4th non-coding RNA and epigenetic research experience exchange meeting
Meeting time : 2017.6.10 -6.11
Venue : Guangzhou Science City
Conference website :
Http://
Dr. Gao Ching will be a guest speaker at the 4th non-coding RNA and epigenetic research experience exchange , bringing a wonderful report entitled "Critical roles of long noncoding RNAs in Drosophila spermatogenesis". Dear friends, act quickly!
Qingdao Beautiful Skin Biotechnology Co., Ltd , https://www.hafilleresthetic.com