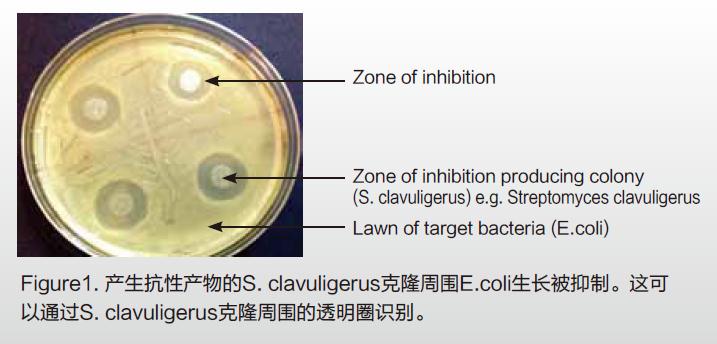
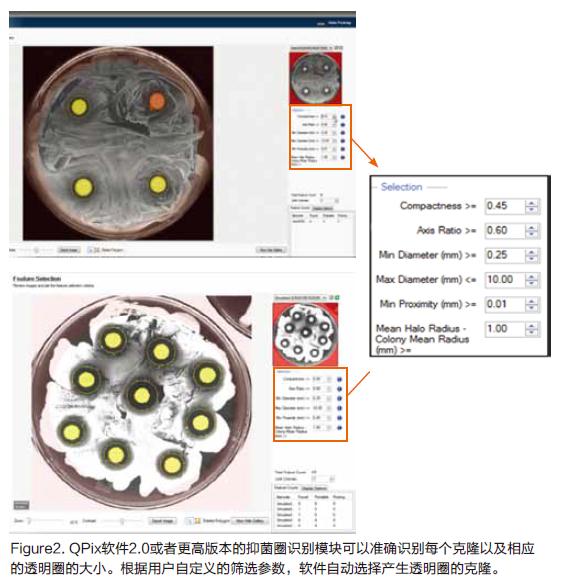

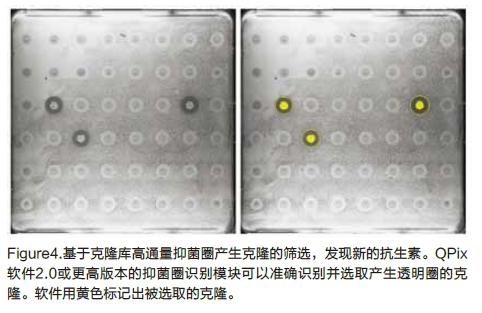
Probiotics are a class of active microorganisms that are beneficial to the host by colonizing the human body and changing the composition of the flora in a certain part of the host. By regulating the immune function of the host mucosa and system or by regulating the balance of intestinal flora, promoting nutrient absorption and maintaining intestinal health, resulting in the production of single microorganisms or mixed microorganisms with well-defined composition that are beneficial to health.
Probiotics,Probiotic Efficacy,Probiotic vitamins,Probiotic Health Supplements
YT(Xi'an) Biochem Co., Ltd. , https://www.ytlinkherb.com