Cucumber is popular among consumers. It is a kind of high-yield vegetable. The high-quality variety is disease-resistant, high-quality, high-yield, strong in resistance, good in commodity, resistant to storage and transportation, stable in production, suitable for producers and consumers. The variety required.

1 seedling
1.1 Nursery facility selection
According to different seasons, greenhouses, plastic sheds, impotence, hotbeds and other nursery facilities are selected. Conditional seedling seedlings and factory seedlings can be used, and the nursery facilities can be disinfected to create environmental conditions suitable for seedling growth and development.
1.2 Nutritional soil preparation
Nutrient soil requirements: pH 5.5 ~ 7.5, organic matter 2.5% ~ 3%, organic phosphorus 20 ~ 40 mg / kg, quick-acting potassium 100 ~ 140 mg / kg, alkaline nitrogen 120 ~ 150 mg / kg. The porosity is about 60%, the soil is loose, and the fertilizer and water retention performance are good. The prepared nutrient soil is evenly spread on the seeding bed or placed in a nutrient bowl with a thickness of 10 cm. Factoryized tray or nutrient seedling nutrient soil formula: 2 parts of grass charcoal plus 1 part of vermiculite, and an appropriate amount of decomposed farmyard manure.
Ordinary seedbed or nutrition nursery nutrient soil formula: nutrient soil can be used in 6 fields of straw soil (preferably onion or charcoal soil), 3 parts of decomposed organic fertilizer, 1 part of decomposed horse manure, and add appropriate amount in nutrient soil. Superphosphate, diammonium phosphate. It is not advisable to use unfermented farmyard manure. The root regeneration ability of cucumber is weak. Plastic or earthworms should be used for seedlings. The prepared nutritious soil should be stacked in a warm place for 7 to 10 days and then installed (or placed in a nursery bed). The nutrient soil is 1 to 1.5 cm away from the mouth. Pre-set the nutrition é’µ, cover 1 to 2 layers of mulch to increase the ground temperature. If the ground temperature is too low, the heating line can be used to warm up.
Disinfection of nursery bed soil: 30 to 50 ml of formalin per square meter of seeding bed, add 3 liters of water, spray the bed soil, cover with plastic film for 3 days, peel off the film, wait until the gas is exhausted, or 72.2% downy mildew 400 times of water-repellent agent; or seedlings mixed with soil, 50-80 grams per cubic meter, fully mixed, can prevent seedling disease, blight and so on.
Seed treatment. Soaking seeds: soak seeds with 50% carbendazim WP 500 times for 1 hour, or soak seeds with formalin 300 times for 1.5 hours. Washing and germination can prevent blight and black spot disease. Soaking in warm soup: Put the dried seeds into warm water at 55-60 °C for about 10 minutes. The treatment should be stirred continuously. When the water temperature drops to 28-30 °C, soak for 4-6 hours. Germination: After soaking the seeds, remove the seeds and put them in the leaching water and place them at 28-30 °C to germination. During the germination process, turn them 2 or 3 times to make the heat even, increase the oxygen permeability and prevent mold. When the seeds are white, they are placed at a low temperature of -1 to 0 °C for 12 to 24 hours to increase the cold resistance of the seedlings.
According to the cultivation season, the seedling raising method and the strong seedling index, the appropriate sowing date is selected. The amount of seedlings per 100 square meters of cultivation area is 100-150 grams, and the amount used for live broadcast is 200-300 grams. 25 to 30 grams per square meter of seed bed.
1.3 Seedling management
Temperature: Summer and autumn seedlings rely on sunshade to cool down. Illumination: Winter and spring seedlings use light curtains or light-filling facilities to increase light. Ventilation: Proper ventilation, reduce temperature and humidity. After the first true leaf is unfolded, the seedlings are treated with large temperature difference, and the temperature difference is maintained at 5-8 °C. Watering is appropriate depending on the season and lyrics. The seedling stage is dominated by water control and fertilizer control. When the seedlings are 3 to 4 leaves, 0.3% urea can be chased in combination with the seedlings. When the seed is arched, a layer of sieved soil is sprinkled to accelerate the shell detachment. Expand the nutrient area: expand the seedling distance when the seedlings are 2 to 3 leaves. Refining seedlings: winter and spring seedlings, one week before planting, 20 to 23 °C during the day and 10 to 12 °C during the night. Spray 75% chlorothalonil once a day before planting.
1.4 Grafting
Grafting method: The grafting method, the cucumber is planted 2 to 3 days earlier than the pumpkin, and grafted when the cucumber has true leaves exposed. Plug in, the pumpkin is sown 3 to 4 days earlier than the cucumber. In the pumpkin cotyledons, there is a first true leaf, and the two cotyledons of the cucumber are grafted together.
Management of grafted seedlings: Grafted seedlings are planted into a nutrient bowl with a diameter of 10 cm, covering the small arch shed for 2 to 3 days to improve the temperature and humidity to facilitate wound healing. After 7 to 10 days, the scion grows new leaves and the small arch shed is removed. The standard of strong seedlings: cotyledons intact, stem base thick, leaf color dark green, no pests and diseases. Early spring seedlings, plant height of about 15 cm, 4 to 5 true leaves.
2 Preparation before planting
2.1 Site preparation of base fertilizer
The farmyard manure and chemical fertilizer applied to the base fertilizer can not be applied, and all of them are applied. The quality of farmyard manure is more than 5,000 kg per mu, 30-35 kg of nitrogen fertilizer, 50 kg of phosphate fertilizer, or 15 kg of diammonium. Continuously deep in two times to achieve the purpose of full-layer fertilization. Cucumber production adheres to organic fertilizer, base fertilizer, phased topdressing, strict control of chemical fertilizers, especially the use of nitrogen fertilizer, and the use of nitrate nitrogen fertilizer and chlorine nitrogen fertilizer are prohibited.

2.2 shed disinfection
The shed should be disinfected before planting. Each 667 square meters of facilities should be mixed with sawdust by using 80% of 80% dichlorvos emulsifiable concentrate, mixed with 2000-3000 grams of sulphur powder, ignited in 10 places, sealed for a day and night, and planted after odorless.
3 colonization
3.1 Colonization time
The minimum soil temperature of 10 cm is stable through 10 °C, the daytime temperature reaches about 20 °C for more than 6 hours, the nighttime minimum temperature is above 6-8 °C, and it is stable after about 1 week.
3.2 Colonization methods and density
Planted in a single row, the plant spacing is 30 cm × 70 cm, covering the mulch. It adopts double-row colonization, the distance between the two rows is 40-50 cm, the distance between the two rows is 75-80 cm, the spacing between plants is 28-30 cm, and generally 3000-4000 plants are planted per 667 square meters.
4 Field management
4.1 Temperature
Slow seedling period: no more than 35 °C during the day and no less than 12 °C at night. If the temperature is too low, a small arch shed can be added at the beginning of the planting. Temperature management after slow seedling: The temperature in sunny morning should be stable at around 30 °C, time is 5-6 hours, and it drops to 20-25 °C in the afternoon. It stays at 16-17 °C in the middle of the night and 11-13 °C in the middle of the night.
4.2 Lighting
Use a light-transparent weather-resistant functional film to keep the film surface clean, uncover the insulation cover during the day, and hang the reflective curtain at the back of the solar greenhouse to maximize the light intensity and time. Air humidity: According to the requirements of humidity and the need to control diseases in different growth stages of cucumber, the optimal index of relative air relative humidity is 80% to 90% in the slow seedling period and 70% to 85% in the flowering and melon period. Production requirements are controlled by the ground cover, drip irrigation or dark irrigation, ventilation and moisture removal, temperature control and other measures to control the best indicators. Carbon dioxide: Carbon dioxide is added in winter and spring to achieve a concentration of 800-1000 mg/kg in the facility.
4.3 Fertilizer and water management
Under-film drip irrigation or dark irrigation. Watering in time after planting, watering the seedling water for 3~5 days, after the root melon is sitting, the seedlings are finished, watering and topdressing, no water in the winter and spring, no watering in the hot noon or afternoon, the relative humidity of the soil is kept. 60% to 70%, 75% to 85% in summer and autumn. If the melon seedling is sick, it must be cured first, then watered after 2 to 3 days. According to the cucumber phase and growth period, fertilize according to the requirements of balanced fertilization, and timely apply nitrogen and potassium fertilizer. After the root melon is harvested, the fertilizer is topdressed twice with water, and each application of ferric ammonium is 15-20 kg per acre. After large ventilation, it should be topdressed twice. Urea or human excrement can be used. Human excrement should be applied for about 1000 kg per mu. At the beginning of the melon period, foliar top dressing is carried out with 0.2% potassium dihydrogen phosphate solution every 7 to 10 days, and 0.2% diammonium phosphate solution can also be used.
Fertilizers not allowed: Urban waste, sludge and organic fertilizers that have not been harmlessly treated and have excessive levels of heavy metals and elements should not be used in production.
4.4 Plant adjustment
Hanging vines or inserting vines: Use nylon rope to hang vines or use thin bamboo rafts to tie vines. Topping and bottoming: Main vines, combined with vines, remove the tendrils in time and remove the side vines from the roots. The middle and upper side vines can leave a melon and a leaf topping. The main vine grows to the top of the frame, and the plants reach 25 to 28 pieces. When the true leaves are topped or placed, the old yellow leaves, diseased leaves and old leaves should be removed in the middle and late stages of the melon, and the deformed melon should be destroyed in time.
4.5 Ventilation management
The greenhouse is mainly based on natural ventilation. After the cucumbers are planted in the greenhouse, the early ventilation is only through the door wind. The lower half of the door should be blocked by the door panel or the straw curtain to prevent the wind and the seedlings from being damaged. When there is no wind on sunny days, it should be ventilated early. In windy days, it should be ventilated at night. After each irrigation, the shed should be warmed up to 30 °C, and then kept for 1 hour before ventilation. In rainy and rainy days, it should be ventilated and dehydrated to prevent too much cooling. 1 to 2 hours of dehumidification, then close for 3 to 4 hours, take measures to open and close, ventilation in the rain to prevent vents from entering the water, to avoid creating conditions for the occurrence of downy mildew and other diseases.
4.6 Timely harvesting
Pick the root melon early in time to prevent falling. Timely batch harvesting, reducing plant burden, to ensure the quality of commercial fruit, and promote fruit expansion in the later period. Product quality should meet the requirements of pollution-free food. Clean the garden: clean up the leaves and weeds, concentrate on the harmless treatment, and keep the garden clean.
4.7 Pest Control
1 Main pests and diseases in seedling stage: rickets, blight, mites. 2 Main pests and diseases in the field: downy mildew, bacterial angular leaf spot, anthracnose, black spot disease, powdery mildew, blight, blight, blight, gray mold, sclerotinia, viral disease, mites, whitefly, Bemisia tabaci, root knot nematode, sassafras, leaf miner. Principles of prevention and control: In accordance with the plant protection policy of “prevention first, comprehensive preventionâ€, adhere to the principle of harmless treatment of “agricultural prevention, physical control, biological control, and chemical prevention and treatmentâ€.
4.7.1 Agricultural control: create suitable reproductive environment conditions: cultivate age-appropriate seedlings, improve stress resistance; control temperature and air humidity, suitable fertilizer and water, sufficient light and carbon dioxide, adjust air by wind and paving, adjust different Suitable temperature during the growth period, avoid low temperature and high temperature barriers; deep ditch sorghum, prevent water accumulation, clean the countryside, so as to be conducive to plant growth and development, to avoid invasive diseases.
4.7.2 Farming Reform: Rotating with non-melon crops for more than three years. Water and drought rotation is carried out in areas where conditions permit.
4.7.3 Scientific fertilization: Balance soil fertilization, increase the application of fully decomposed organic fertilizer, reduce fertilizer application, and prevent soil salinization.

4.7.4 Physical control: 1 Facility protection: closed at the air outlet with insect net. 2 yellow board trapping: hanging yellow boards in the facility to trap insects such as aphids. The yellow plate is 25 cm × 40 cm and is suspended for 30 to 40 pieces per 667 square meters. 3 silver ash film to avoid mites: paving silver mulch film or hanging silver ash film strip to avoid cockroaches. 4 high temperature disinfection: the greenhouse should be used for high temperature disinfection of the soil in summer. High temperature shack to control cucumber downy mildew: choose sunny morning, pour a large amount of water, close the shed, increase the shed temperature to 46 ~ 48 ° C for 2 hours, then slowly increase the wind vent from the top, slowly lower the room temperature . If you need to swell every 15 days later. Strengthen the management of fertilizer and water after the shack. 5 insecticidal lamp traps pests: use frequency vibration insecticidal lamps, black light lamps, high pressure mercury lamps, double wave lamps to trap pests.
4.7.5 Biological control: 1 natural enemy: actively protect and use natural enemies to prevent pests and diseases. 2 biological agents: powdery mildew, gray mold, black spot disease can choose 4% agricultural anti-120 water 200 times solution, or 1% agricultural anti-wuyimycin 150 ~ 200 times liquid control. Use 72% agricultural streptomycin sulfate 4000-5000 times solution to control bacterial diseases, control aphids, whitefly, use 1.8% Aifuding emulsifiable concentrate 3000 times solution, use 10% Liuyangmycin emulsifiable concentrate 1000 times solution to control cockroach pests .
4.7.6 Chemical control of main pests and diseases: Chemical control should meet the requirements of GB4285 and GB/T8321 (all parts). The dust protection method and the smoke extraction method are preferred for the protection. Pay attention to the rotation of drugs, and mix them reasonably. Strictly control the safety interval of pesticides.
4.7.7 It is not allowed to use highly toxic and highly toxic pesticides: Methamidophos, methyl-to-sulfuric acid, parathion, monocrotophos, phospho-amine, phorate, methylisophosphorus, and tertidine are not allowed in production. Sulfuric acid, methylthiophosphorus, guanidine phosphorus, internal phosphorus, carbofuran, aldicarb, chlorpyrifos, thiophosphorus, fly phos, chlorpyrifos, chlorpyrifos, benzene phosphate Poisonous, highly toxic pesticides.
In the early stage of the downy mildew disease, the shed was sealed and shed before and after sunset. 45% of chlorothalonil smoke agent 667 square meters used in a dose of 250 to 300 grams. Place the smoke agent evenly on the floor and ignite with an incense or cigarette. The ignition sequence is sequentially ignited from the shed to the shed. After burning the smoke agent in the shed, at least the shack should be sealed for more than 4 hours. The time for smog is best to be carried out before and after sunset. The next day, the louver and vents are fully opened for ventilation. In the early stage of blight, 50% carbendazim WP 600 times or 70% thiophanate-methyl WP 800 times solution should be used for rooting. Each root should be sprayed with 200 ml. For the prevention and control of powdery mildew and gray mold, you can choose 65% methicillin WP 800 times or 28% ash WP 1500 times.
The above is the main content of high-quality and efficient planting technology and pest control in greenhouses, especially the introduction of pest control. The farmers who need it can come to Huinong.com.
New product of U85 micro laser distance sensors use highly focused class 2 laser to detect objects or measure distances, and can return a measured value via varieties intface( serial, usb, rs232, rs485, bluetooth etc.). The electronic distance sensor is a very small Laser Distance Sensor, but high resolution up to 1mm and long distance measuring sensor - teachable measuring range of up to 30m. Extremely accurate distance sensing sensors, errors down to ± 1mm. And the mini sensors and measurements support continuous measurement function, great for compact solutions(eg: robots) with the smallest Laser Distance Sensor of the world!
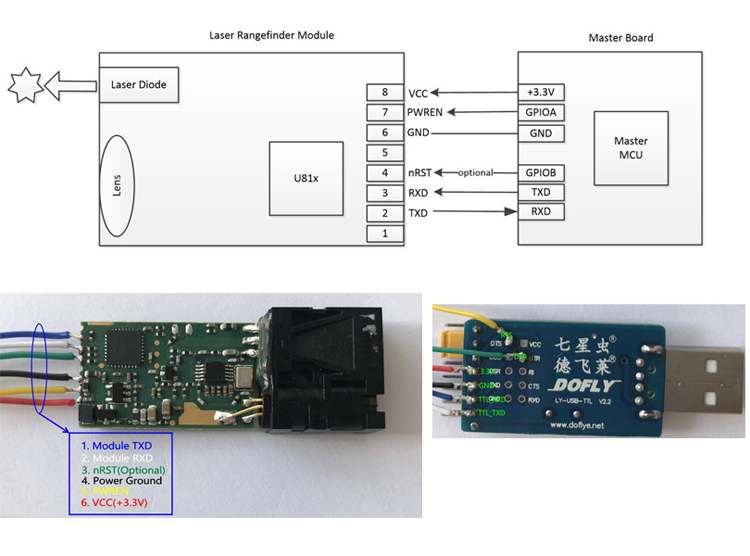
Parameters of U85:
Accuracy
±1 mm (0.04 inch)
Measuring Unit
mm
Measuring Range (without Reflection)
0.03-20m/0.03-30m
Measuring Time
0.1~3 seconds
Laser Class
Class II
Laser Type
620nm-690nm, <1mW
Size
41*17*7mm (±1 mm)
Weight
About 4g
Voltage
DC2.0~3V
Electrical Level
TTL/CMOS
Certifications
CTNT, FDA, CE, FCC, RoHS, etc.
Operating Temperature
0-40 ℃ (32-104 ℉ )
Storage Temperature
-25~60 ℃ (-13~140 ℉)
Mini Laser Distance Sensor,Optical Laser Distance Sensor,Smallest Laser Range Sonsor,Laser Measuring Sensor
Chengdu JRT Meter Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.rangesensors.com